what is all this smog stuff? what are "cats"?
Catalytic Converters
Here's a dump on how much of the emissions control equipment works...
Thermactor Air System
Some review of how it works...
Revised 17-Sept-2011 to add testing procedure.
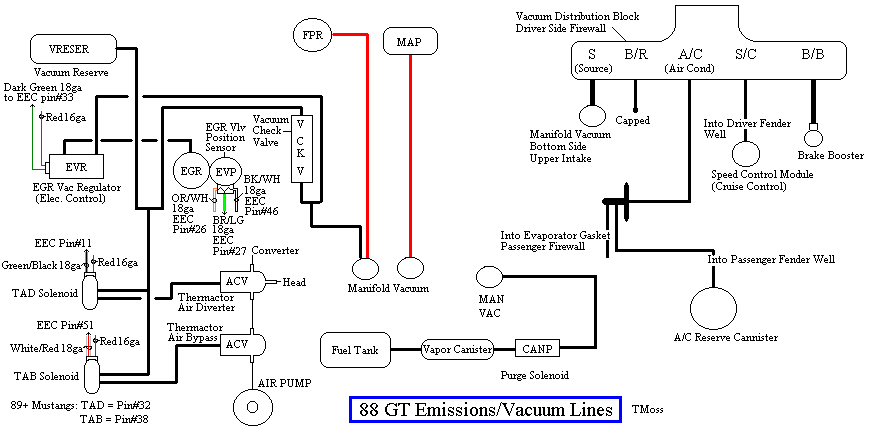
The Thermactor air pump (smog pump) supplies air to the heads or catalytic converters. This air helps break down the excess HC (hydrocarbons) and CO (carbon monoxide). The air supplied to the catalytic converters helps create the catalytic reaction that changes the HC & CO into CO2 and water vapor. Catalytic converters on 5.0 Mustangs are designed to use the extra air provided by the smog pump. Without the extra air, the catalytic converters will clog and fail.
The Thermactor air pump draws air from an inlet filter in the front of the pump. The smog pump puts air into the heads when the engine is cold and then into the catalytic converters when it is warm. The Thermactor control valves serve to direct the flow. The first valve, TAB (Thermactor Air Bypass) or AM1 valve) either dumps air to the atmosphere or passes it on to the second valve. The second valve, TAD (Thermactor Air Diverter valve or AM2 valve) directs it to the heads or the catalytic converters. Check valves located after the TAB & TAD solenoids prevent hot exhaust gases from damaging the control valves or pump in case of a backfire. The air serves to help consume any unburned hydrocarbons by supplying extra oxygen to the catalytic process. The computer tells the Thermactor Air System to open the Bypass valve at WOT (wide open throttle) minimizing engine drag. This dumps the pump's output to the atmosphere, and reduces the parasitic drag caused by the smog pump to about 2-4 HP at WOT. The Bypass valve also opens during deceleration to reduce or prevent backfires.
Code 44 RH side air not functioning.
Code 94 LH side air not functioning.
The computer uses the change in the O2 sensor readings to detect operation of the Thermactor control valves. When the dump valve opens, it reduces the O2 readings in the exhaust system. Then it closes the dump valve and the O2 readings increase. By toggling the dump valve (TAB), the computer tests for the 44/94 codes.
Failure mode is usually due to a clogged air crossover tube, where one or both sides of the tube clog with carbon. The air crossover tube mounts on the back of the cylinder heads and supplies air to each of the Thermactor air passages cast into the cylinder heads. When the heads do not get the proper air delivery, they set codes 44 & 94, depending on which passage is clogged. It is possible to get both 44 & 94, which would suggest that the air pump or control valves are not working correctly, or the crossover tube is full of carbon or missing.
Computer operation & control for the Thermactor Air System
Automobile computers use current sink technology. They do not source power to any relay, solenoid or actuator like the IAC, fuel pump relay, or fuel injectors. Instead the computer provides a ground path for the positive battery voltage to get back to the battery negative terminal. That flow of power from positive to negative is what provides the energy to make the IAC, fuel pump relay, or fuel injectors work. No ground provided by the computer, then the actuators and relays don't operate.
One side of the any relay/actuator/solenoid in the engine compartment will be connected to a red wire that has 12-14 volts anytime the ignition switch is in the run position. The other side will have 12-14 volts when the relay/actuator/solenoid isn't turned on. Once the computer turns on the clamp side, the voltage on the computer side of the wire will drop down to 1 volt or less.
In order to test the TAD/TAB solenoids, you need to ground the white/red wire on the TAB solenoid or the light green/black wire on the TAD solenoid.
For 94-95 cars: the colors are different. The White/Red wire (TAB control) is White/Orange (Pin 31 on the PCM). The Green/Black wire (TAD control) should be Brown (pin 34 at the PCM). Thanks to HISSIN50 for this tip.
Testing the system:
To test the computer, you can use a test light across the TAB or TAD wiring connectors and dump the codes. When you dump the codes, the computer does a self test that toggles every relay/actuator/solenoid on and off. When this happens, the test light will flicker.
Disconnect the big hose from smog pump: with the engine running you should feel air output. Reconnect the smog pump hose & apply vacuum to the first vacuum controlled valve: Its purpose is to either dump the pump's output to the atmosphere or pass it to the next valve.
The next vacuum controlled valve directs the air to either the cylinder heads when the engine is cold or to the catalytic converter when the engine is warm. Disconnect the big hoses from the back side of the vacuum controlled valve and start the engine. Apply vacuum to the valve and see if the airflow changes from one hose to the next.
The two electrical controlled vacuum valves mounted on the rear of the passenger side wheel well turn the vacuum on & off under computer control. Check to see that both valves have +12 volts on the red wire. Then ground the white/red wire and the first solenoid should open and pass vacuum. Do the same thing to the light green/black wire on the second solenoid and it should open and pass vacuum.
Remember that the computer does not source power for any actuator or relay, but provides the ground necessary to complete the circuit. That means one side of the circuit will always be hot, and the other side will go to ground or below 1 volt as the computer switches on that circuit.
The computer provides the ground to complete the circuit to power the solenoid valve that turns the
vacuum on or off. The computer is located under the passenger side kick panel. Remove the kick panel & the cover over the computer wiring connector pins. Check Pin 38 Solenoid valve #1 that provides vacuum to the first Thermactor control valve for a switch from 12-14 volts to 1 volt or less. Do the same with pin 32 solenoid valve #2 that provides vacuum to the second Thermactor control valve. Starting the engine with the computer jumpered to self test mode will cause all the actuators to toggle on and off. If after doing this and you see no switching of the voltage on and off, you can start testing the wiring for shorts to ground and broken wiring. An Ohm check to ground with the computer connector disconnected & the solenoid valves disconnected should show open circuit between the pin 32 and ground and again on pin 38 and ground. In like manner, there should be less than 1 ohm between pin 32 and solenoid valve #2 and pin 38 & Solenoid valve #1.
If after checking the resistance of the wiring & you are sure that there are no wiring faults, start looking at the solenoid valves. If you disconnect them, you can jumper power & ground to them to verify operation. Power & ground supplied should turn on the vacuum flow, remove either one and the vacuum should stop flowing.
Typical resistance of the solenoid valves is in the range of 20-70 Ohms.
Theory of operation:
Catalytic converters consist of two different types of catalysts: Reduction and Oxidation.
The Reduction catalyst is the first converter in a 5.0 Mustang, and the Oxidation converter is the second converter. The Oxidation converter uses the extra air from the smog pump to burn the excess HC. Aftermarket converters that use the smog pump often combine both types of catalysts in one housing. Since all catalytic reactions depend on heat to happen, catalytic converters do not work as efficiently with long tube headers. The extra length of the long tubes reduces the heat available to operate the O2 sensors and the catalytic converters. That will cause emissions problems, and reduce the chances of passing an actual smog test.
Now for the Chemistry...
"The reduction catalyst is the first stage of the catalytic converter. It uses platinum and rhodium to help reduce the NOx emissions. When an NO or NO2 molecule contacts the catalyst, the catalyst rips the nitrogen atom out of the molecule and holds on to it, freeing the oxygen in the form of O2. The nitrogen atoms bond with other nitrogen atoms that are also stuck to the catalyst, forming N2. For example:
2NO => N2 + O2 or 2NO2 => N2 + 2O2
The oxidation catalyst is the second stage of the catalytic converter. It reduces the unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide by burning (oxidizing) them over a platinum and palladium catalyst. This catalyst aids the reaction of the CO and hydrocarbons with the remaining oxygen in the exhaust gas. For example:
2CO + O2 => 2CO2
There are two main types of structures used in catalytic converters -- honeycomb and ceramic beads. Most cars today use a honeycomb structure." Quote courtesy of How Stuff Works (
HowStuffWorks "Catalysts")
What happens when there is no extra air from the smog pump...
As engines age, the quality of tune decreases and wear causes them to burn oil. We have all seem cars that go down the road puffing blue or black smoke from the tailpipe. Oil consumption and poor tune increase the amount of HC the oxidation catalyst has to deal with. The excess HC that the converters cannot oxidize due to lack of extra air becomes a crusty coating inside the honeycomb structure. This effectively reduces the size of the honeycomb passageways and builds up thicker over time and mileage. Continuous usage under such conditions will cause the converter to fail and clog. The extra air provided by the Thermactor Air System (smog pump) is essential for the oxidation process. It oxidizes the added HC from oil consumption and poor tune and keeps the HC levels within acceptable limits.
Newer catalytic converters do not use the Thermactor Air System (smog pump) because they are designed to work with an improved computer system that runs leaner and cleaner
They add an extra set of O2 sensors after the catalytic converters to monitor the oxygen and HC levels. Using this additional information, the improved computer system adjusts the air/fuel mixture for cleaner combustion and reduced emissions. If the computer cannot compensate for the added load of emissions due to wear and poor tune, the catalytic converters will eventually fail and clog. The periodic checks (smog inspections) are supposed to help owners keep track of problems and get them repaired. Use them on an 86-95 Mustang and you will slowly kill them with the pollutants that they are not designed to deal with.
Some basic theory to clarify how things work is in order…
EGR System theory and testing
Revised 29-Sep-2013 to add code definitions for EGR sensor and EVR regulator.
The EGR shuts off at Wide Open Throttle (WOT), so it has minimal effect on performance. The addition of exhaust gas drops combustion temperature, increases gas mileage and reduces the tendency of the engine to ping. It can also reduce HC emissions by reducing fuel consumption. The primary result of EGR usage is a reduction in NOx emissions. It does this by reducing the amount of air/fuel mixture that gets burned in the combustion process. Less air from the intake system means less air to mx with the fuel, so the computer leans out the fuel delivery calculations to balance things out. This reduces combustion temperature, and the creation of NOx gases. The reduced combustion temp reduces the tendency to ping.
The computer shuts down the EGR system when it detects WOT (Wide Open Throttle), so the effect on full throttle performance is too small to have any measurable negative effects.
The EGR system has a vacuum source (line from the intake manifold) that goes to the EVR, computer operated electronic vacuum regulator. The EVR is located on the back of the passenger side shock strut tower. The computer uses RPM, Load. and some other factors to tell the EVR to pass vacuum to open the EGR valve. The EGR valve and the passages in the heads and intake manifold route exhaust gas to the EGR spacer (throttle body spacer). The EGR sensor tells the computer how far the EGR valve is open. Then computer adjusts the signal sent to the EVR to hold, increase or decrease the vacuum. The computer adds spark advance to compensate for the recirculated gases and the slower rate they burn at.
The resistor packs used to fool the computer into turning off the CEL (Check Engine Light) off are a bad idea. All they really do is mess up the data the computer uses to calculate the correct air/fuel mixture. You can easily create problems that are difficult to pin down and fix.
Troubleshooting:
There should be no vacuum at the EGR valve when at idle. If there is, the EVR (electronic vacuum regulator) mounted on the backside of the passenger side wheelwell is suspect. Check the vacuum line plumbing to make sure the previous owner didn’t cross the vacuum lines.
Diagram courtesy of Tmoss & Stang&2birds. (the diagram says 88 GT, but the EGR part is the same for 86-93 Mustangs)
The EGR sensor is basically a variable resistor, like the volume control on a radio. One end is 5 volt VREF power from the computer (red/orange wire). One end is computer signal ground (black/white), and the middle wire (brown/lt green) is the signal output from the EGR sensor. It is designed to always have some small voltage output from it anytime the ignition switch is the Run position. That way the computer knows the sensor & the wiring is OK. No voltage on computer pin 27 (brown/lt green wire) and the computer thinks the sensor is bad or the wire is broken and sets code 31. The voltage output can range from approximately .6-.85 volt. A defective or missing sensor will set codes 31 (EVP circuit below minimum voltage) or 32 ( EGR voltage below closed limit).
The EVR regulates vacuum to the EGR valve to maintain the correct amount of vacuum. The solenoid coil should measure 20-70 Ohms resistance. The regulator has a vacuum feed on the bottom which draws from the intake manifold. The other vacuum line is regulated vacuum going to the EGR valve. One side of the EVR electrical circuit is +12 volts anytime the ignition switch is in the run position. The other side of the electrical circuit is the ground path and is controlled by the computer. The computer switches the ground on and off to control the regulator solenoid. A defective EVR will set codes 33 (insufficient flow detected), 84 (EGR Vacuum Regulator failure – Broken vacuum lines, no +12 volts, regulator coil open circuit, missing EGR vacuum regulator.)
EGR test procedure courtesy of cjones
To check the EGR valve:
Bring the engine to normal temp.
Connect a vacuum pump to the EGR Valve or
see the EGR test jig drawing below. Connnect the test jig or to directly to manifold vacuum.
Do not connect the EGR test jig to the EVR (Electronic Vacuum Regulator).
Apply 5in vacuum to the valve.
Using the test jig, use your finger to vary the vacuum
If the engine stumbled or died then EGR Valve and passage(there is a passageway through the heads and intake) are good.
If the engine did NOT stumble or die then either the EGR Valve is bad and/or the passage is blocked.
If the engine stumbled,
connect EGR test jig to the hose coming off of the EGR Valve.
Use your finger to cap the open port on the vacuum tee.
Snap throttle to 2500 RPM (remember snap the throttle don't hold it there).
Did the vacuum gauge show about 2-5 in vacuum?
If not the EVR has failed
EGR test jig
To test the computer and wiring to the computer, you can use a test light across the EVR wiring connectors and dump the codes. When you dump the codes, the computer does a self test that toggles every relay/actuator/solenoid on and off. When this happens, the test light will flicker. If the test light remains on the computer or the wiring is suspect.
To check the EVR to computer wiring, disconnect the EVR connector and connect one end of the Ohmmeter to the dark green wire EVR wiring. Remove the passenger side kick panel and use a 10 MM socket to remove the computer connector from the computer. Set the Ohmmeter to high range and connect the other ohmmeter lead to ground. You should see an infinite open circuit indication or a reading greater than 1 Meg Ohm. If you see less than 200 Ohms, the dark green wire has shorted to ground somewhere.