Code 14 - Ignition pickup (PIP) was erratic – the hall effect sensor in the distributor is failing. Bad sensor, bad wiring, dirty contacts.
The PIP is a Hall Effect magnetic sensor that triggers the TFI and injectors. There is a shutter wheel alternately covers and uncovers a fixed magnet as it rotates. The change in the magnetic field triggers the sensor. They are often heat sensitive, increasing the failure rate as the temperature increases.
The PIP sensor is mounted in the bottom of the distributor under the shutter wheel. In stock Ford distributors, you have to press the gear off the distributor shaft to get access to it to replace it. Most guys just end up replacing the distributor with a reman unit for about $75 exchange
Code 34 Or 334 - EGR voltage above closed limit - Failed sensor, carbon between EGR pintle valve and seat holding the valve off its seat or vacuum control problems. Remove the EGR valve and clean it with carbon remover. Prior to re-installing see if you can blow air through the flange side of the EGR by mouth. If it leaks, there is carbon stuck on the pintle valve seat, replace the EGR valve ($85-$95).
Vacuum control problems:
If someone has misrouted the EGR vacuum plumbing or the EVR (Electronic Vacuum Regulator) has failed, you can get this code.
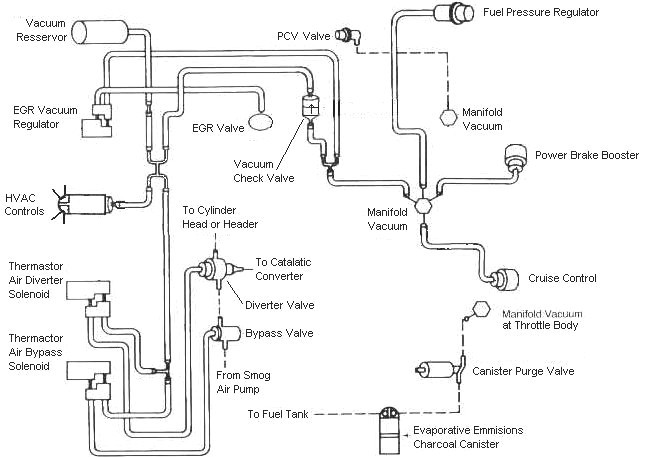
Diagram courtesy of Tmoss & Stang&2birds
EGR test procedure courtesy of cjones
to check the EGR valve:
bring the engine to normal temp.
connect a vacuum pump to the EGR Valve or
see the EGR test jig drawing below. Connnect the test jig or to directly to manifold vacuum.
Do not connect the EGR test jig to the EVR (Electronic Vacuum Regulator).
apply 5in vacuum to the valve.
Using the test jig, use your finger to vary the vacuum
if engine stumbled or died then EGR Valve and passage(there is a passageway through the heads and intake) are good.
if engine did NOT stumble or die then either the EGR Valve is bad and/or the passage is blocked.
if engine stumbled,
connect EGR test jig to the hose coming off of the EGR Valve.
Use your finger to cap the open port on the vacuum tee.
snap throttle to 2500 RPM (remember snap the throttle don't hold it there).
did the vacuum gauge show about 2-5 in vacuum?
if not the EVR has failed
EGR test jig
If the blow by test passes, and you have replaced the sensor, then you have electrical ground problems. Check the resistance between the black/white wire on the MAP/BARO sensor and then the black/white wire on the EGR and the same wire on the TPS. It should be less than 1.5 ohm. Next check the resistance between the black/white wire and the negative battery post. It should be less than 1.5 ohm.
Note that all resistance tests must be done with power off. Measuring resistance with a circuit powered on will give false readings and possibly damage the meter.
Let’s put on our Inspector Gadget propeller head beanies and think about how this works:
The EGR sensor is a variable resistor with ground on one leg and Vref (5 volts) on the other. Its’ resistance ranges from 4000 to 5500 Ohms measured between Vref & ground, depending on the sensor. The center connection of the variable resistor is the slider that moves in response to the amount of vacuum applied. The slider has some minimum value of resistance greater than 100 ohms so that the computer always sees a voltage present at its’ input. If the value was 0 ohms, there would be no voltage output. Then the computer would not be able to distinguish between a properly functioning sensor and one that had a broken wire or bad connection. The EGR I have in hand reads 700 Ohms between the slider (EPV) and ground (SIG RTN) at rest with no vacuum applied. The EGR valve or sensor may cause the voltage to be above closed limits due to the manufacturing tolerances that cause the EGR sensor to rest at a higher position than it should.
The following sensors are connected to the white 10 pin connector (salt & pepper engine harness connectors)
This will affect idle quality by diluting the intake air charge
See the following website for some help from Tmoss (diagram designer) & Stang&2Birds (website host) for help on 88-95 wiring Mustang FAQ - Engine Information Everyone should bookmark this site.
Ignition switch wiring
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/IgnitionSwitchWiring.gif
Fuel, alternator, A/C and ignition wiring
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/fuel-alt-links-ign-ac.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for 88-91 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/88-91_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for 91-93 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/91-93_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for94-95 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/94-95_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Vacuum diagram 89-93 Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/mustangFoxFordVacuumDiagram.jpg
HVAC vacuum diagram
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/Mustang_AC_heat_vacuum_controls.gif
TFI module differences & pinout
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/TFI_5.0_comparison.gif
Fuse box layout
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/MustangFuseBox.gif
Codes 44 & 94 - AIR system inoperative - Air Injection. Check vacuum lines for leaks, & cracks.
Revised 28-Oct-2009 to correct code definitions and operation.
Code 44 RH side air not functioning.
Code 94 LH side air not functioning.
The computer uses the change in the O2 sensor readings to detect operation of the Thermactor control valves. When the dump valve opens, it reduces the O2 readings in the exhaust system. Then it closes the dump valve and the O2 readings increase. By toggling the dump valve (TAB), the computer tests for the 44/94 codes.
Failure mode is usually due to a clogged air crossover tube, where one or both sides of the tube clog with carbon. The air crossover tube mounts on the back of the cylinder heads and supplies air to each of the Thermactor air passages cast into the cylinder heads. When the heads do not get the proper air delivery, they set codes 44 & 94, depending on which passage is clogged. It is possible to get both 44 & 94, which would suggest that the air pump or control valves are not working correctly, or the crossover tube is full of carbon or missing.
Testing the system:
Disconnect the big hose from smog pump: with the engine running you should feel air output. Reconnect
the smog pump hose & apply vacuum to the first vacuum controlled valve: Its purpose is to either dump
the pump's output to the atmosphere or pass it to the next valve.
The next vacuum controlled valve directs the air to either the cylinder heads when the engine is cold or
to the catalytic converter when the engine is warm. Disconnect the big hoses from the back side of the
vacuum controlled valve and start the engine. Apply vacuum to the valve and see if the airflow changes
from one hose to the next.
The two electrical controlled vacuum valves mounted on the rear of the passenger side wheel well turn the
vacuum on & off under computer control. Check to see that both valves have +12 volts on the red wire.
Then ground the white/red wire and the first solenoid should open and pass vacuum. Do the same thing to
the light green/black wire on the second solenoid and it should open and pass vacuum.
Remember that the computer does not source power for any actuator or relay, but provides the ground
necessary to complete the circuit. That means one side of the circuit will always be hot, and the other side
will go to ground or below 1 volt as the computer switches on that circuit.
The computer provides the ground to complete the circuit to power the solenoid valve that turns the
vacuum on or off. The computer is located under the passenger side kick panel. Remove the kick panel &
the cover over the computer wiring connector pins. Check Pin 38 Solenoid valve #1 that provides vacuum
to the first Thermactor control valve for a switch from 12-14 volts to 1 volt or less. Do the same with pin
32 solenoid valve #2 that provides vacuum to the second Thermactor control valve. Starting the engine
with the computer jumpered to self test mode will cause all the actuators to toggle on and off. If after
doing this and you see no switching of the voltage on and off, you can start testing the wiring for shorts to
ground and broken wiring. An Ohm check to ground with the computer connector disconnected & the
solenoid valves disconnected should show open circuit between the pin 32 and ground and again on pin 38
and ground. In like manner, there should be less than 1 ohm between pin 32 and solenoid valve #2 and pin
38 & Solenoid valve #1.
If after checking the resistance of the wiring & you are sure that there are no wiring faults, start looking at the
solenoid valves. If you disconnect them, you can jumper power & ground to them to verify operation. Power &
ground supplied should turn on the vacuum flow, remove either one and the vacuum should stop flowing.
Typical resistance of the solenoid valves is in the range of 20-70 Ohms.
See the following website for some help from Tmoss (diagram designer) & Stang&2Birds (website host)
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/fuel-alt-links-ign-ac.gif
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/88-91eecPinout.gif
See
http://forums.stangnet.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=50636&d=1180923382 for a very nice drawing of the Thermactor Air System (smog pump) plumbing
If you have a catalytic converter H pipe, you need to fix these codes. If you don't, then don't worry about them