Code 22 or 126 MAP (vacuum) or BARO signal out of range. The MAP or BARO sensor is pretty much the same sensor for both Mass Air & Speed Density cars. The main difference is where it is connected. Mass Air cars vent it to the atmosphere, while Speed Density cars connect it to the intake manifold vacuum. Its purpose is to help set a baseline for the air/fuel mixture by sensing changes in barometric pressure. The MAP or BAP sensor puts out a 5 volt square wave that changes frequency with variations in atmospheric pressure. The base is 154 HZ at 29.92" of mercury - dry sunny day at sea level, about 68-72 degrees. You need an oscilloscope or frequency meter to measure it. There a very few DVM with a price tag under $40 that will measure frequency, but there are some out there.
The MAP/BARO sensor is mounted on the firewall behind the upper manifold on 86-93 Mustangs.
Baro or MAP test using frequency meter - run the test key on engine off. The noise from the ignition system will likely upset the frequency meter. I used a 10 x oscilloscope probe connected from the frequency meter to the MAP/BAP to reduce the jitter in the meter's readout.
If it is defective, your air/fuel ratio will be off and the car’s performance & emissions will suffer
Some basic checks you can make to be sure that the sensor is getting power & ground:
Note that all resistance tests must be done with power off. Measuring resistance with a circuit powered on will give false readings and possibly damage the meter.
Check the resistance between the black/white wire on the MAP/BARO sensor and then the black/white wire on the EGR and the same wire on the TPS. It should be less than 1 ohm. Next check the resistance between the black/white wire and the negative battery cable. It should be less than 1.5 ohm.
The following power on check requires you to turn the ignition switch to the Run position.
Use a DVM to check for 5 volts on the orange/white wire. If it is missing, look for +5 volts at the orange/white wire on the TPS or EGR sensors. Use the black/white wire for the ground for the DVM.
Code 32 – EGR voltage below closed limit. Vref (5 volt reference voltage supplied by the computer) missing or broken wire or bad connection in circuit. Use a DVM to check for 5 volts on the orange/white wire. If it is missing, look for +5 volts at the orange/white wire on the TPS or MAP sensor located on the firewall near the center of the car. Use the black/white wire for the ground for the DVM.
Let’s put on our Inspector Gadget propeller head beanies and think about how this works:
The EGR sensor is a variable resistor with ground on one leg and Vref (5 volts) on the other. Its’ resistance ranges from 4000 to 5500 Ohms measured between Vref & ground, depending on the sensor. The center connection of the variable resistor is the slider that moves in response to the amount of vacuum applied. The slider has some minimum value of resistance greater than 100 ohms so that the computer always sees a voltage present at its’ input. If the value was 0 ohms, there would be no voltage output. Then the computer would not be able to distinguish between a properly functioning sensor and one that had a broken wire or bad connection. The EGR I have in hand reads 700 Ohms between the slider (EPV) and ground (SIG RTN) at rest with no vacuum applied.
As vacuum is applied, the voltage on the slider increases (EVP). As the voltage increases, the computer knows the how much the EGR valve is opened and how much exhaust gas is being recirculated. It uses the load table to calculate the amount of exhaust gas required depending on RPM, Mass Air Flow, ACT, ECT & TPS. It then sends a signal to the Electronic Vacuum Regulator to hold, increase or decrease the vacuum being applied to the EGR valve.
Theory class is over now, let’s spin up our propeller head beanies and get with it… Go Gadget, Go…
Measure the resistance of the EGR sensor between the two end pins. You should see between 3500 to 5500 Ohms. With the sensor removed, measure the resistance again while pressing on the plunger. You should see the resistance drop from its high value to a low reading of 200-700 ohms depending on the sensor. No resistance readings, or values way out of range, the sensor is bad.
If the Orange white wire has Vref, (5 volts =/-.25 volt) then you have some wiring problems because the computer isn’t seeing the minimum voltage on the EVR pin. Ohm the wiring back to the computer. Check for resistance between the brown/lt green wire on the EGR sensor and pin 27 on the computer: you should have less than 1 ohm. Repeat the process for the orange/white wire and pin 26. Do it again between the black/white wire and pin 46. In no case should you have more than 1 ohm. Remember that resistance checks are always done with the power off the circuit.
Voltage and resistance checks are good: Here’s an EGR test procedure I copied from cjones
EGR test procedure
to check the EGR valve:
bring the engine to normal temp.
connect a vacuum pump to the EGR Valve or
see the EGR test jig drawing below. Connnect the test jig or to directly to manifold vacuum.
Do not connect the EGR test jig to the EVR (Electronic Vacuum Regulator).
apply 5in vacuum to the valve.
Using the test jig, use your finger to vary the vacuum
if engine stumbled or died then EGR Valve and passage(there is a passageway through the heads and intake) are good.
if engine did NOT stumble or die then either the EGR Valve is bad and/or the passage is blocked.
if engine stumbled,
connect EGR test jig to the hose coming off of the EGR Valve.
Use your finger to cap the open port on the vacuum tee.
snap throttle to 2500 RPM (remember snap the throttle don't hold it there).
did the vacuum gauge show about 2-5 in vacuum?
if not the EVR has failed
EGR test jig
t.
If the test procedure fails to provide proper vacuum, check vacuum feed lines for cracks & damage. If the vacuum lines are good, check the electrical wiring to the EVR. If the EVR electrical wiring is good, look for 12 volts on the red wire for the EVR. If the 12 volts is good, look for a varying voltage on the dark green wire on the EVR. Case of last resort, replace the EVR and then the computer
Code 51 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor signal is/was too high -
Possible bad ECT sensor, or wiring. Possible missing signal ground –
black/wire wire broken or bad connection. With the power off, measure the
resistance between the black/white wire and battery ground. You should see
less than 1 ohm. Check the same black /white wire on the TPS and MAP
sensor. More than 1 ohm there and the wire is probably broken in the harness
between the engine and the computer. The 10 pin connectors pass the
black/white wire back to the computer, and can cause problems.
Pin 7 on the computer - ECT signal in. at 176 degrees F it should be .80 volts
Voltages may be measured across the ECT by probing the connector from the rear.
Use care in doing it so that you don't damage the wiring or connector.
50 degrees F = 3.52 v
68 degrees F = 3.02 v
86 degrees F = 2.62 v
104 degrees F = 2.16 v
122 degrees F = 1.72 v
140 degrees F = 1.35 v
158 degrees F = 1.04 v
176 degrees F = .80 v
194 degrees F = .61
212 degrees F = .47 v
230 degrees F = .36 v
248 degrees F = .28 v
Ohms measures at the computer with the computer disconnected, or at the sensor with the sensor disconnected.
50 degrees F = 58.75 K ohms
68 degrees F = 37.30 K ohms
86 degrees F = 27.27 K ohms
104 degrees F = 16.15 K ohms
122 degrees F = 10.97 K ohms
140 degrees F = 7.60 K ohms
158 degrees F = 5.37 K ohms
176 degrees F = 3.84 K ohms
194 degrees F = 2.80 K ohms
212 degrees F = 2.07 K ohms
230 degrees F = 1.55 K ohms
248 degrees F = 1.18 k ohms
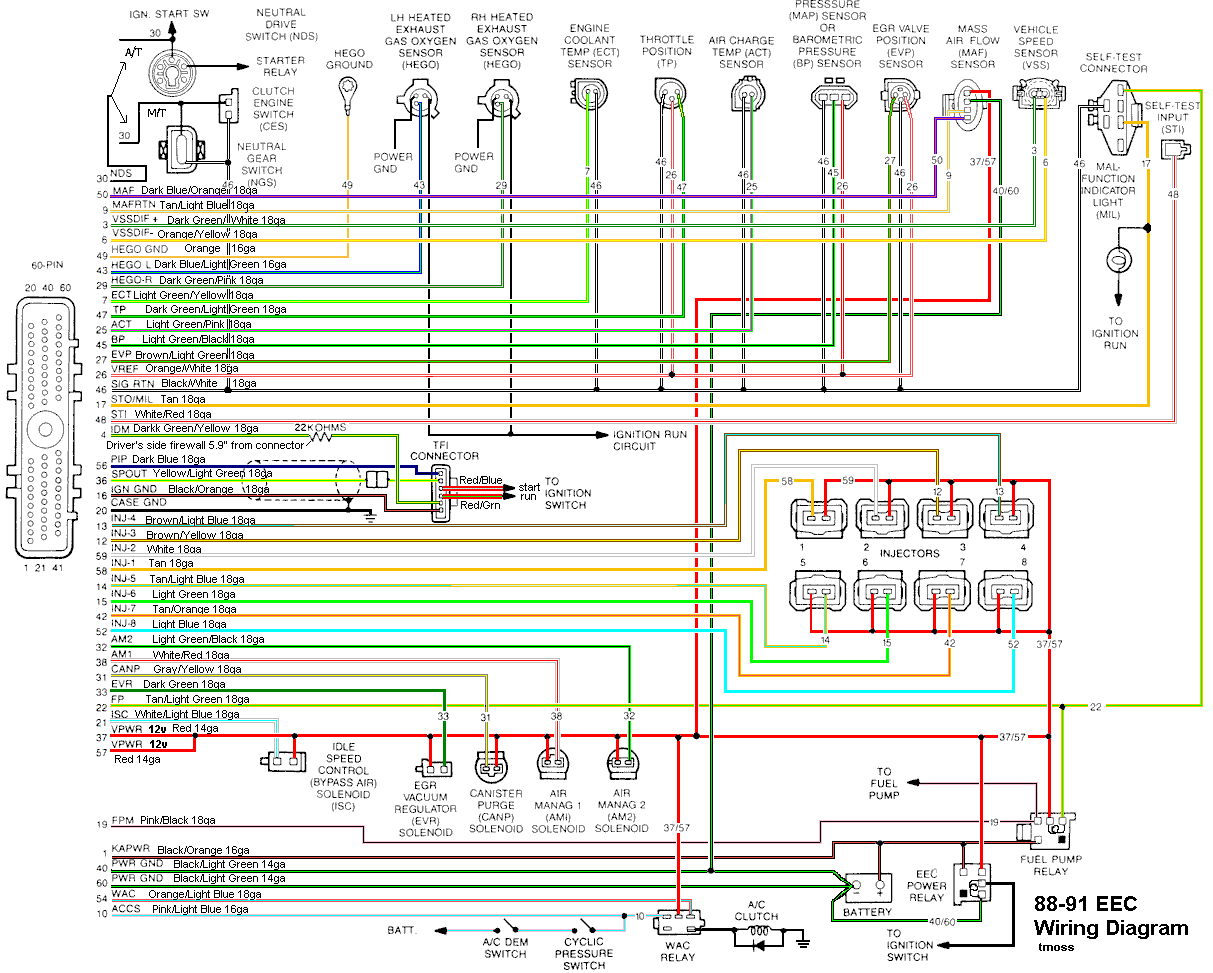
Diagram courtesy of Tmoss & Stang&2birds
See the following website for some help from Tmoss (diagram designer) & Stang&2Birds (website host) for help on 88-95 wiring
Mustang FAQ - Engine Information
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/IgnitionSwitchWiring.gif
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/fuel-alt-links-ign-ac.gif
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/88-91_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Code 53 - Throttle Position sensor too high – TPS – TPS out of adjustment, bad connections, missing signal ground, bad sensor.
Wire colors & functions:
Orange/white = 5 volt VREF from the computer
Dark Green/lt green = TPS output to computer
Black/white = Signal ground from computer
Always use the Dark green/lt green & Black/white wires to set the TPS base voltage.
Do the test with the ignition switch in the Run position without the engine running.
Use the Orange/white & Black white wires to verify the TPS has the correct 5 volts source from the computer.
Setting the TPS: you'll need a good Digital Voltmeter (DVM) to do the job. Set the TPS voltage at .5- 1.1 range. Because of the variables involved with the tolerances of both computer and DVM, I would shoot for somewhere between .6 and 1.0 volts. Unless you have a Fluke or other high grade DVM, the second digit past the decimal point on cheap DVM’s is probably fantasy. Since the computer zeros out the TPS voltage every time it powers up, playing with the settings isn't an effective aid to performance or drivability. The main purpose of checking the TPS is to make sure it isn't way out of range and causing problems.
The Orange/White wire is the VREF 5 volts from the computer. You use the Dark Green/Lt green wire (TPS signal) and the Black/White wire (TPS ground) to set the TPS. Use a pair of safety pins to probe the TPS connector from the rear of the connector. You may find it a little difficult to make a good connection, but keep trying. Put the safety pins in the Dark Green/Lt green wire and Black/White wire. Make sure the ignition switch is in the Run position but the engine isn't running.
Here’s a TPS tip I got from NoGo50
When you installed the sensor make sure you place it on the peg right and then tighten it down properly. Loosen the back screw a tiny bit so the sensor can pivot and loosen the front screw enough so you can move it just a little in very small increments. I wouldn’t try to adjust it using marks.
(copied from MustangMax, Glendale AZ)
A.) Always adjust the TPS and Idle with the engine at operating temp. Dive it around for a bit if you can and get it nice and warm.
B.) When you probe the leads of the TPS, do not use an engine ground, put the ground probe into the lead of the TPS. You should be connecting both meter probes to the TPS and not one to the TPS and the other to ground.
C.) Always reset the computer whenever you adjust the TPS or clean/change any sensors. I just pull the battery lead for 10 minutes.
D.) The key is to adjust the TPS voltage and reset the computer whenever the idle screw is changed.
The TPS is a variable resistor, must like the volume control knob on a cheap radio. We have all heard them crackle and pop when the volume is adjusted. The TPS sensor has the same problem: wear on the resistor element makes places that create electrical noise. This electrical noise confuses the computer, because it expects to see a smooth increase or decrease as the throttle is opened or closed.
TPS testing: most of the time a failed TPS will set code 23 or 63, but not always. Use either an analog meter or a DVM with an analog bar graph and connect the leads as instructed above. Turn the ignition switch to the Run position, but do not start the engine. Note the voltage with the throttle closed. Slowly open the throttle and watch the voltage increase smoothly, slowly close the throttle and watch the voltage decrease smoothly. If the voltage jumps around and isn’t smooth, the TPS has some worn places in the resistor element. When the throttle is closed, make sure that the voltage is the same as what it was when you started. If it varies more than 10%, the TPS is suspect of being worn in the idle range of its travel.
Adjusting the TPS fails to resolve the problem:
Check the black/white wire resistance. Connect one ohmmeter lead to the black/white wire on the TPS and one lead to the negative post on the battery. You should see less than 1.5 ohm, more than that indicates a problem.
Always take resistance measurements with the circuit powered off.
Clean the 10 pin salt & pepper shaker connectors.
.
See
Ford Fuel Injection 10-pin Connector Fix for more help
Code 54 – ACT sensor out of range. Broken or damaged wiring, bad ACT sensor. Note that that if the outside air temp is below 50 degrees F that the test for the ACT can be in error.
Check the resistance of the black/white wire to battery ground. If it is less than 1.5 ohm, it is good. If it is more than 1.5 ohm, the black/white wire has bad connections or a broken wire. Always take resistance measurements with the circuit powered off.
Then check the resistance of the ACT sender located in the #5 intake runner on most 5.0 stangs.
ACT & ECT test data:
The ACT & ECT have the same thermistor, so the table values are the same
Pin 7 on the computer - ECT signal in. at 176 degrees F it should be .80 volts
Pin 25 on the computer - ACT signal in. at 50 degrees F it should be 3.5 volts. It is a good number if the ACT is mounted in the inlet airbox. If it is mounted in the lower intake manifold, the voltage readings will be lower because of the heat transfer. Here's the table :
68 degrees F = 3.02 v
86 degrees F = 2.62 v
104 degrees F = 2.16 v
122 degrees F = 1.72 v
140 degrees F = 1.35 v
158 degrees F = 1.04 v
176 degrees F = .80 v
194 degrees F = .61
Ohms measures at the computer with the computer disconnected, or at the sensor with the sensor disconnected.
50 degrees F = 58.75 K ohms
68 degrees F = 37.30 K ohms
86 degrees F = 27.27 K ohms
104 degrees F = 16.15 K ohms
122 degrees F = 10.97 K ohms
140 degrees F = 7.60 K ohms
158 degrees F = 5.37 K ohms
176 degrees F = 3.84 K ohms
194 degrees F = 2.80 K ohms
Code 67 - clutch not depressed (5 speed) or car not in neutral or park (auto) or A/C in On position when codes
where dumped. Possible neutral safety switch or wiring problem. This code may prevent you from running the Key On
Engine On tests. You can generally ignore this code, since it has no effect on engine performance.
The computer wants to make sure the A/C is off due to the added load on the engine for the engine running tests. It also
checks to see that the transmission is in Neutral or the clutch depressed (T5, T56, Tremec 3550 & TKO). This prevents
the diagnostics from being run when the car is driven. Key On Engine Running test mode takes the throttle control away
from the driver for several tests. This could prove hazardous if the computer was jumpered into test mode and then driven.
The NSS code 67 can be bypassed for testing. You will need to temporarily ground computer pin 30 to the chassis.
Computer pin 30 uses a Lt blue/yellow wire. Remove the passenger side kick panel and then remove the plastic cover from
the computer wiring connector. Use a safety pin to probe the connector from the rear. Jumper the safety pin to the
The codes 32, 51, 53, & 54 suggest a bad or missing signal ground in the engine fuel injector or computer wiring harness. You may find that the MAP sensor ground is also bad.
Troubleshooting loss of signal ground on 91-93 Mustangs.
The computer pin 46 signal ground is a critical component: it provides ground for the MAP/BARO, TPS, ECT, EGR position sensor and ACT. Signal ground is used in many circuits that have analog inputs to isolate the electrical noise. It is always separate from power ground, although both may have a common connection origination point. Signal ground usually has some conditioning that reduces the electrical noise to prevent false readings
The black/white or gray/red wire (pin 46) is signal ground for the computer. In 91-93 model cars it is black/white on the engine mounted sensors (EGR, ACT, ECT, & TPS) and grey/red on under hood diagnostic connector, Baro and Neutral Safety Switch.
It provides a dedicated ground for the EGR, Baro, ACT, ECT, & TPS sensors as well as the ground to put the computer into self test mode. If this ground is bad, none of the sensors mentioned will work properly. That will severely affect the car's performance. You will have hard starting, low power and drivability problems. What sometimes happens is that the test connector black/white wire gets jumpered to power which either burns up the wiring or burns the trace off the pc board inside the computer. That trace connects pins 46 to pins 40 & 60. Only an experienced electronics technician can open the computer up & repair the trace if it burns up and creates an open circuit.
If the ground for the TPS goes bad, the TPS output voltage increases and the idle speed goes up.
Troubleshooting signal ground problems:
Note that all resistance tests must be done with power off. Measuring resistance with a circuit powered on will give false readings and possibly damage the meter.
1.) With the power off, measure the resistance between the computer test ground
gray/red wire) on the self test connector and battery ground. You should see less than
2.0 ohms. More than 2.0 ohms indicates a wiring problem or an open circuit inside the computer as described above.
2.) MAP circuit: Check the resistance between the gray/red wire on the MAP/BARO sensor and then the black/white wire on the EGR and the same wire on the TPS. It should be less than 1 ohms. Higher resistance than 1 ohms indicates a problem with the 10 pin connector or the splice inside the main harness where the wire from the 10 pin connectors joins the rest of the black/white wire. Next check the resistance between the gray/red wire and the negative battery cable. It should be less than 2.0 ohms. If the resistance check in step 1 was good this one should be too. More than 2.0 ohms indicates a wiring problem or an open circuit inside the computer as described above.
3.) Engine mounted sensor circuit: Check the resistance between the black/white wire on the TPS and battery ground. It should be less than 2.0 ohms. Higher resistance than 2.0 ohms indicates a problem with the 10 pin connector or the splice inside the main harness where the wire from the 10 pin connectors joins the rest of the gray/red wire.
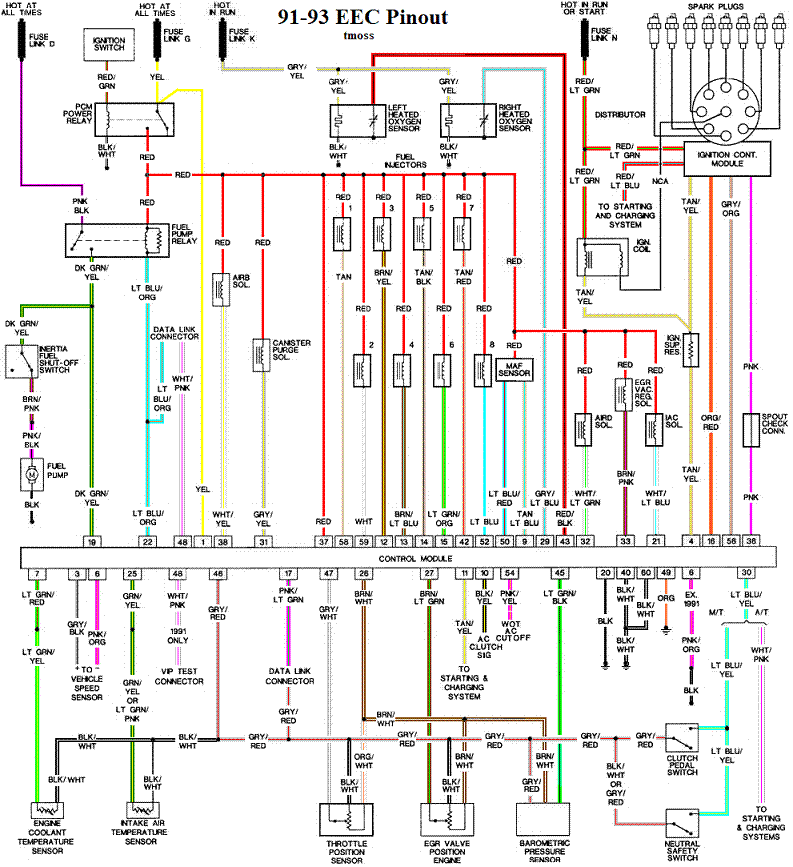
Diagram courtesy of Tmoss & Stang&2birds
See the following website for some help from Tmoss (diagram designer) & Stang&2Birds
(website host) for help on 86-95 5.0 Mustang wiring Mustang FAQ - Engine Information Everyone should bookmark this site.
Ignition switch wiring
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/IgnitionSwitchWiring.gif
Fuel, alternator, A/C and ignition wiring
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/fuel-alt-links-ign-ac.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for 88-91 5.0 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/88-91_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for 91-93 5.0 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/91-93_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for 94-95 5.0 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/94-95_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Vacuum diagram 89-93 Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/mustangFoxFordVacuumDiagram.jpg
HVAC vacuum diagram
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/Mustang_AC_heat_vacuum_controls.gif
TFI module differences & pinout
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/TFI_5.0_comparison.gif
Fuse box layout
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/MustangFuseBox.gif