CODE: 31 (KOEO) - EVP circuit below minimum voltage. Vref (5 volt reference voltage supplied by the computer) missing or broken wire or bad connection in circuit. Use a DVM to check for 5 volts on the orange/white wire. If it is missing, look for +5 volts at the orange/white wire on the TPS or MAP sensor located on the firewall near the center of the car. Use the black/white wire for the ground for the DVM.
With the sensor removed from the EGR and still connected, press the plunger and watch the voltage change on the brown/lt green wire. Pull the passenger side kick panel and measure the voltage at the computer. You will need to remove the plastic cover over the wires and probe them from the backside. A safety pin may prove very useful for this task. Use pin 27, EVR input (brown/lt green wire) and pin 46, signal ground (black/white wire) to measure the voltage. The orange/white wire is Vref and should always be 5 volts -/+ .25 volt. Be sure to measure Vref at the EGR sensor to rule out any broken wires or bad connections.
Measuring the voltage at the computer helps you spot broken wiring and intermittent connections.
See the graphic for the 10 pin connector circuit layout.
Some basic theory to clarify how things work is in order…
EGR System theory and testing
The EGR shuts off at Wide Open Throttle (WOT), so it has minimal effect on performance. The addition of exhaust gas drops combustion temperature, increases gas mileage and reduces the tendency of the engine to ping. It can also reduce HC emissions by reducing fuel consumption. The primary result of EGR usage is a reduction in NOx emissions. It does this by reducing the amount of air/fuel mixture that gets burned in the combustion process. This reduces combustion temperature, and the creation of NOx gases. The reduced combustion temp reduces the tendency to ping.
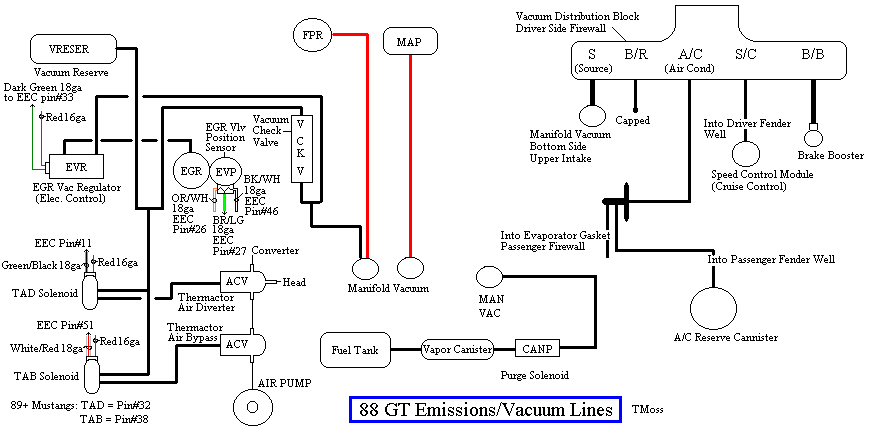
The EGR system has a vacuum source (line from the intake manifold) that goes to the EVR, computer operated electronic vacuum regulator. The EVR is located on the back of the passenger side shock strut tower. The computer uses RPM, Load. and some other factors to tell the EVR to pass vacuum to open the EGR valve. The EGR valve and the passages in the heads and intake manifold route exhaust gas to the EGR spacer (throttle body spacer). The EGR sensor tells the computer how far the EGR valve is open. Then computer adjusts the signal sent to the EVR to hold, increase or decrease the vacuum. The computer adds spark advance to compensate for the recirculated gases and the slower rate they burn at.
Troubleshooting:
There should be no vacuum at the EGR valve when at idle. If there is, the EVR (electronic vacuum regulator) mounted on the backside of the passenger side wheelwell is suspect. Check the vacuum line plumbing to make sure the previous owner didn’t cross the vacuum lines.
Diagram courtesy of Tmoss & Stang&2birds. (the diagram says 88 GT, but the EGR part is the same for 86-93 Mustangs)
The EGR sensor is basically a variable resistor, like the volume control on a radio. One end is 5 volt VREF power from the computer (red/orange wire). One end is computer signal ground (black/white), and the middle wire (brown/lt green) is the signal output from the EGR sensor. It is designed to always have some small voltage output from it anytime the ignition switch is the Run position. That way the computer knows the sensor & the wiring is OK. No voltage on computer pin 27 (brown/lt green wire) and the computer thinks the sensor is bad or the wire is broken and sets code 31. The voltage output can range from approximately .6-.85 volt.
The EVR regulates vacuum to the EGR valve to maintain the correct amount of vacuum. The solenoid coil should measure 20-70 Ohms resistance. The regulator has a vacuum feed on the bottom which draws from the intake manifold. The other vacuum line is regulated vacuum going to the EGR valve. One side of the EVR electrical circuit is +12 volts anytime the ignition switch is in the run position. The other side of the electrical circuit is the ground path and is controlled by the computer. The computer switches the ground on and off to control the regulator solenoid.
EGR test procedure courtesy of cjones
To check the EGR valve:
Bring the engine to normal temp.
Connect a vacuum pump to the EGR Valve or
see the EGR test jig drawing below. Connnect the test jig or to directly to manifold vacuum.
Do not connect the EGR test jig to the EVR (Electronic Vacuum Regulator).
Apply 5in vacuum to the valve.
Using the test jig, use your finger to vary the vacuum
If the engine stumbled or died then EGR Valve and passage(there is a passageway through the heads and intake) are good.
If the engine did NOT stumble or die then either the EGR Valve is bad and/or the passage is blocked.
If the engine stumbled,
connect EGR test jig to the hose coming off of the EGR Valve.
Use your finger to cap the open port on the vacuum tee.
Snap throttle to 2500 RPM (remember snap the throttle don't hold it there).
Did the vacuum gauge show about 2-5 in vacuum?
If not the EVR has failed
EGR test jig
To test the computer and wiring to the computer, you can use a test light across the EVR wiring connectors and dump the codes. When you dump the codes, the computer does a self test that toggles every relay/actuator/solenoid on and off. When this happens, the test light will flicker. If the test light remains on the computer or the wiring is suspect.
To check the EVR to computer wiring, disconnect the EVR connector and connect one end of the Ohmmeter to the dark green wire EVR wiring. Remove the passenger side kick panel and use a 10 MM socket to remove the computer connector from the computer. Set the Ohmmeter to high range and connect the other ohmmeter lead to ground. You should see an infinite open circuit indication or a reading greater than 1 Meg Ohm. If you see less than 200 Ohms, the dark green wire has shorted to ground somewhere.
Late Model Restoration may still have the Ford Racing M-12071-N302 kit with the EGR valve & sensor along with the ACT & ECT sensors for $45. See
http://www.latemodelrestoration.com/iwwida.pvx?;item?item_no=M12071N302 1&comp=LRS for more details