well i broke one ground that goes from the tranny to driverside firewall. putting my engine back together and just trying to make sure i have all grounds hooked up. and are there alternate places to put my grounds? this is my first engine build. need to know where ALL grounds go
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
engine ground locations
- Thread starter warriorpluto
- Start date
-
Sponsors (?)
Grounds are important to any electrical system, and especially to
computer controlled engines. In an automobile, the ground is
the return path for power to get back to the alternator and battery.
1.) The main power ground is from engine block to battery: it is
the power ground for the starter & alternator.
2.) The secondary power ground is between the back of the
intake manifold and the driver's side firewall. It is often missing or
loose. It supplies ground for the alternator, A/C compressor
clutch and other electrical accessories such as the gauges.
Any car that has a 3G or high output current alternator needs
a 4 gauge ground wire running from the block to the chassis
ground where the battery pigtail ground connects.
The 3G has a 130 amp capacity, so you wire the power side
with 4 gauge wire. It stands to reason that the ground side
handles just a much current, so it needs to be 4 gauge too.
The picture shows the common ground point for the battery & extra 3G
alternator ground wire as described above in paragraph 2. A screwdriver
points to the bolt that is the common ground point.
The battery common ground is a 10 gauge pigtail with the computer ground
attached to it.
Picture courtesy timewarped1972

Correct negative battery ground cable.

3.) The computer has its own dedicated power ground that comes off the ground pigtail
on the battery ground wire. Due to it's proximity to the battery, it may become
corroded by acid fumes from the battery.
In 86-90 model cars, it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/lt green wire.
In 91-95 model cars it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/white wire.
You'll find it up next to the starter solenoid where the wire goes into the wiring harness.
4.) All the sensors have a common separate ground. This
includes the TPS, ACT, EGE, BAP, & VSS sensors.
5.) The O2 sensor heaters have their own ground (HEGO ground)
coming from the computer. This is different and separate from
the O2 sensor ground. It is an orange wire with a ring terminal
on it. It is located in the fuel injector wiring harness and comes out
under the throttle body. It gets connected to a manifold or bolt on
back of the cylinder head.
6.) The TFI module has 2 grounds: one for the foil shield around
the wires and another for the module itself. The TFI module
ground terminates inside the computer.
7.) The computer takes the shield ground for the TFI module and
runs it from pin 20 to the chassis near the computer.
8.) The computer's main power ground (the one that comes from
the battery ground wire) uses pins 40 & 60 for all the things it
controls internally.
See Automotive Test Tools
for help troubleshooting voltage drops across grounds
Extra grounds are like the reserve parachute for a sky diver.
If the main one fails, there is always your reserve.
The best plan is to have all the grounds meet at one central spot
and connect together there. That eliminates any voltage drops
from grounds connected at different places. A voltage drop
between the computer ground and the alternator power ground will effectively
reduce the voltage available to the computer by the amount of the drop.
computer controlled engines. In an automobile, the ground is
the return path for power to get back to the alternator and battery.
1.) The main power ground is from engine block to battery: it is
the power ground for the starter & alternator.
2.) The secondary power ground is between the back of the
intake manifold and the driver's side firewall. It is often missing or
loose. It supplies ground for the alternator, A/C compressor
clutch and other electrical accessories such as the gauges.
Any car that has a 3G or high output current alternator needs
a 4 gauge ground wire running from the block to the chassis
ground where the battery pigtail ground connects.
The 3G has a 130 amp capacity, so you wire the power side
with 4 gauge wire. It stands to reason that the ground side
handles just a much current, so it needs to be 4 gauge too.
The picture shows the common ground point for the battery & extra 3G
alternator ground wire as described above in paragraph 2. A screwdriver
points to the bolt that is the common ground point.
The battery common ground is a 10 gauge pigtail with the computer ground
attached to it.
Picture courtesy timewarped1972

Correct negative battery ground cable.

3.) The computer has its own dedicated power ground that comes off the ground pigtail
on the battery ground wire. Due to it's proximity to the battery, it may become
corroded by acid fumes from the battery.
In 86-90 model cars, it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/lt green wire.
In 91-95 model cars it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/white wire.
You'll find it up next to the starter solenoid where the wire goes into the wiring harness.
4.) All the sensors have a common separate ground. This
includes the TPS, ACT, EGE, BAP, & VSS sensors.
5.) The O2 sensor heaters have their own ground (HEGO ground)
coming from the computer. This is different and separate from
the O2 sensor ground. It is an orange wire with a ring terminal
on it. It is located in the fuel injector wiring harness and comes out
under the throttle body. It gets connected to a manifold or bolt on
back of the cylinder head.
6.) The TFI module has 2 grounds: one for the foil shield around
the wires and another for the module itself. The TFI module
ground terminates inside the computer.
7.) The computer takes the shield ground for the TFI module and
runs it from pin 20 to the chassis near the computer.
8.) The computer's main power ground (the one that comes from
the battery ground wire) uses pins 40 & 60 for all the things it
controls internally.
See Automotive Test Tools
for help troubleshooting voltage drops across grounds
Extra grounds are like the reserve parachute for a sky diver.
If the main one fails, there is always your reserve.
The best plan is to have all the grounds meet at one central spot
and connect together there. That eliminates any voltage drops
from grounds connected at different places. A voltage drop
between the computer ground and the alternator power ground will effectively
reduce the voltage available to the computer by the amount of the drop.
Sn95 bryqn
Active User
- Feb 18, 2016
- 11
- 0
- 1
Where are all the ground locations for 95 mustang gt ? Anyone have pictures of o2 sensors ground/s ? Need help making sure i have all grounds correct if anyone can add pictures or detailed information on sn95 ground locations
They have the same grounds and the same locations as the 87-93 Mustangs with a few possible exceptions.Where are all the ground locations for 95 mustang gt ? Anyone have pictures of o2 sensors ground/s ? Need help making sure i have all grounds correct if anyone can add pictures or detailed information on sn95 ground locations
See [http://www.helminc.com/helm/Result....ategory=8&Keyword=&Module=&selected_media=for an EVTM manual for your car. Cost is $21.00 plus shipping
This is one of the best investments you can make!
nickpic
Advanced Member
anyone have a pic of the ground that is supposed to be between the back of the intake manifold and the driver's side firewall?
It isn't anything fancy; just a heavy gauge strap or length of wire with a lug for a bolt on each end. The exact location isn't critical, electrically a block of metal is block of metal.anyone have a pic of the ground that is supposed to be between the back of the intake manifold and the driver's side firewall?
A piece of 4 gauge wire like those used to go between the starter solenoid and the starter is a good choice if you can find a short one. It doesn't have to be insulated either, and that is why the straps with lugs are good.
nickpic
Advanced Member
Well that sounds easy enough then. I am not seeing one on mine so I'll just add one. If the stock one is there, I know it won't hurt to have another one.It isn't anything fancy; just a heavy gauge strap or length of wire with a lug for a bolt on each end. The exact location isn't critical, electrically a block of metal is block of metal.
A piece of 4 gauge wire like those used to go between the starter solenoid and the starter is a good choice if you can find a short one. It doesn't have to be insulated either, and that is why the straps with lugs are good.
Sent from my XT1650 using Tapatalk
Whitecobrafox13
Member
Whitecobrafox13
Member
@Whitecobrafox13
Grounds
This checklist applies to all Mustangs , not just the EFI equipped cars. Some of the wiring will be different on carb cars and carb conversions
Revised 26 –Oct -2016 to add fuel pump ground to the list.
Grounds are important to any electrical system, and especially to computer controlled engines. In an automobile, the ground is the return path for power to get back to the alternator and battery.
Make sure that all the ground places are clean and shiny bare metal: no paint, no corrosion.
1.) The main power ground is from engine block down by the oil filter to battery: it is the power ground for the starter & alternator.
2.) The secondary power ground is between the back of the intake manifold and the driver's side firewall. It is often missing or loose. It supplies ground for the alternator, A/C compressor clutch and other electrical accessories such as the gauges. The clue to a bad ground here is that the temp gauge goes up as you add electrical load such as heater, lights and A/C.
Any car that has a 3G or high output current alternator needs a 4 gauge ground wire running from the block to the chassis ground where the battery pigtail ground connects. The 3G has a 130 amp capacity, so you wire the power side with 4 gauge wire. It stands to reason that the ground side handles just as much current, so it needs to be 4 gauge too.
The picture shows the common ground point for the battery , computer, & extra 3G alternator ground wire as described above in paragraph 2. A screwdriver points to the bolt that is the common ground point.
The battery common ground is a 10 gauge pigtail with the computer ground attached to it.
Picture courtesy timewarped1972

Correct negative battery ground cable.

3.) The computer's main power ground (the one that comes from the battery ground wire) uses pins 40 & 60 for all the things it controls internally: it comes off the ground pigtail on the battery ground wire. Due to its proximity to the battery, it may become corroded by acid fumes from the battery.
In 86-90 model cars, it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/lt green wire.
In 91-95 model cars it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/white wire.
You'll find it up next to the starter solenoid where the wire goes into the wiring harness.
All the grounds listed in items 1,2 & 3 need to bolt to clean, shiny bare metal. A wire brush or some fine sandpaper is the best thing to use to clean the ground connections.
4.) All the sensors have a common separate signal ground. This includes the TPS, ACT, EGR, BAP, & VSS sensors. This ground is inside the computer and connects pin 46 to pins 40 & 60, which are the main computer grounds. If this internal computer ground gets damaged, you won't be able to dump codes and the car will have idle/stall/ performance problems
The following sensors are connected to the white 10 pin connector (salt & pepper engine harness connectors)
which provides a path for the signal ground back to the computer

5.) The O2 sensor heaters have their own ground (HEGO ground) coming from the computer. This is different and separate from the O2 sensor ground. It is an orange wire with a ring terminal on it. It is located in the fuel injector wiring harness and comes out under the throttle body. It gets connected to a manifold or bolt on back of the cylinder head.
6.) The TFI module has 2 grounds: one for the foil shield around the wires and another for the module itself. The TFI module ground terminates inside the computer.
7.) The computer takes the shield ground for the TFI module and runs it from pin 20 to the chassis near the computer.
8.) Fuel pump ground the fuel pump has a ground pigtail the connects to the body under the gas tank. You have to drop the gas tank to see where it bolts to the body.
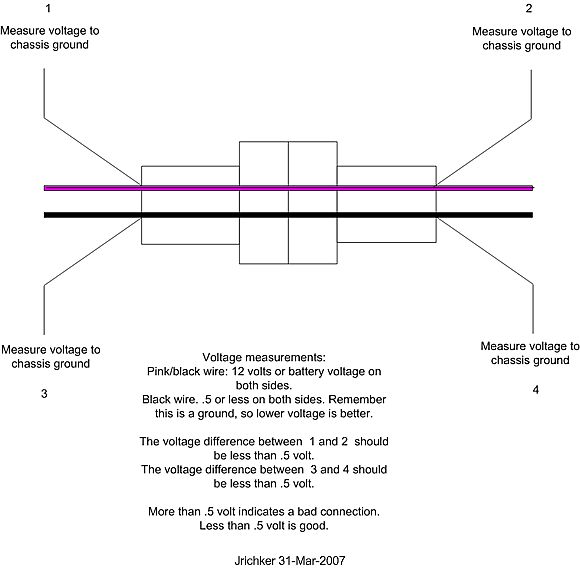
See http://assets.fluke.com/appnotes/automotive/beatbook.pdf for help troubleshooting voltage drops across connections and components. Be sure to have the maximum load on a circuit when testing voltage drops across connections. As current across a defective or weak connection, increases so does the voltage drop. A circuit or connection may check out good with no load or minimal load, but show up bad under maximum load conditions. .
Voltage drops should not exceed the following:
200 mV Wire or cable
300 mV Switch
100 mV Ground
0 mV to <50 mV Sensor Connections
0.0V bolt together connections

Extra grounds are like the reserve parachute for a sky diver. If the main one fails, there is always your reserve.
The best plan is to have all the grounds meet at one central spot and connect together there. That eliminates any voltage drops from grounds connected at different places. A voltage drop between the computer ground and the alternator power ground will effectively reduce the voltage available to the computer by the amount of the drop.
Grounds
This checklist applies to all Mustangs , not just the EFI equipped cars. Some of the wiring will be different on carb cars and carb conversions
Revised 26 –Oct -2016 to add fuel pump ground to the list.
Grounds are important to any electrical system, and especially to computer controlled engines. In an automobile, the ground is the return path for power to get back to the alternator and battery.
Make sure that all the ground places are clean and shiny bare metal: no paint, no corrosion.
1.) The main power ground is from engine block down by the oil filter to battery: it is the power ground for the starter & alternator.
2.) The secondary power ground is between the back of the intake manifold and the driver's side firewall. It is often missing or loose. It supplies ground for the alternator, A/C compressor clutch and other electrical accessories such as the gauges. The clue to a bad ground here is that the temp gauge goes up as you add electrical load such as heater, lights and A/C.
Any car that has a 3G or high output current alternator needs a 4 gauge ground wire running from the block to the chassis ground where the battery pigtail ground connects. The 3G has a 130 amp capacity, so you wire the power side with 4 gauge wire. It stands to reason that the ground side handles just as much current, so it needs to be 4 gauge too.
The picture shows the common ground point for the battery , computer, & extra 3G alternator ground wire as described above in paragraph 2. A screwdriver points to the bolt that is the common ground point.
The battery common ground is a 10 gauge pigtail with the computer ground attached to it.
Picture courtesy timewarped1972

Correct negative battery ground cable.

3.) The computer's main power ground (the one that comes from the battery ground wire) uses pins 40 & 60 for all the things it controls internally: it comes off the ground pigtail on the battery ground wire. Due to its proximity to the battery, it may become corroded by acid fumes from the battery.
In 86-90 model cars, it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/lt green wire.
In 91-95 model cars it is a black cylinder about 2 1/2" long by 1" diameter with a black/white wire.
You'll find it up next to the starter solenoid where the wire goes into the wiring harness.
All the grounds listed in items 1,2 & 3 need to bolt to clean, shiny bare metal. A wire brush or some fine sandpaper is the best thing to use to clean the ground connections.
4.) All the sensors have a common separate signal ground. This includes the TPS, ACT, EGR, BAP, & VSS sensors. This ground is inside the computer and connects pin 46 to pins 40 & 60, which are the main computer grounds. If this internal computer ground gets damaged, you won't be able to dump codes and the car will have idle/stall/ performance problems
The following sensors are connected to the white 10 pin connector (salt & pepper engine harness connectors)
which provides a path for the signal ground back to the computer

5.) The O2 sensor heaters have their own ground (HEGO ground) coming from the computer. This is different and separate from the O2 sensor ground. It is an orange wire with a ring terminal on it. It is located in the fuel injector wiring harness and comes out under the throttle body. It gets connected to a manifold or bolt on back of the cylinder head.
6.) The TFI module has 2 grounds: one for the foil shield around the wires and another for the module itself. The TFI module ground terminates inside the computer.
7.) The computer takes the shield ground for the TFI module and runs it from pin 20 to the chassis near the computer.
8.) Fuel pump ground the fuel pump has a ground pigtail the connects to the body under the gas tank. You have to drop the gas tank to see where it bolts to the body.

See http://assets.fluke.com/appnotes/automotive/beatbook.pdf for help troubleshooting voltage drops across connections and components. Be sure to have the maximum load on a circuit when testing voltage drops across connections. As current across a defective or weak connection, increases so does the voltage drop. A circuit or connection may check out good with no load or minimal load, but show up bad under maximum load conditions. .
Voltage drops should not exceed the following:
200 mV Wire or cable
300 mV Switch
100 mV Ground
0 mV to <50 mV Sensor Connections
0.0V bolt together connections

Extra grounds are like the reserve parachute for a sky diver. If the main one fails, there is always your reserve.
The best plan is to have all the grounds meet at one central spot and connect together there. That eliminates any voltage drops from grounds connected at different places. A voltage drop between the computer ground and the alternator power ground will effectively reduce the voltage available to the computer by the amount of the drop.
Attachments
Similar threads
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 753
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 975
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 1K


